Blog page
Recent Post

Magnets in Restaurant Kitchens

Global supply challenges and HYAB’s role

Electromagnets – a more controllable magnet

Magnetic filtration in the process industry
Sheet metal handling – Easier with magnets

Published: 2025-04-29
![]() Daniel Gårdefelt
Daniel Gårdefelt
Innovative magnetic fastening
We recently published an article about magnetic sheets for printing and another article about magnets for cable management in metal cabinets &nda...
Show more >
Published: 2025-04-24
![]() Daniel Gårdefelt
Daniel Gårdefelt
Magnets in Lithium Batteries – what are they actually used for?
When we think of batteries, magnets might not be the first thing that comes to mind. But in fact, magnets play an important role in the technolog...
Show more >
Published: 2025-01-27
![]() Daniel Gårdefelt
Daniel Gårdefelt
Magnet manufacturing process: From raw material to finished magnet
In today's technology, magnets are in everything from refrigerator magnets/advertising magnets to speakers and sophisticated medical devices...
Show more >
Published: 2023-12-22
![]() Daniel Gårdefelt
Daniel Gårdefelt
Merry Christmas and a Happy New Year!
We thank you all for this year and look forward to 2024 with new business opportunities. As in previous years, this year 2023 we have also collab...
Show more >
Published: 2023-08-28
![]() Daniel Gårdefelt
Daniel Gårdefelt
The role of magnets in high-speed electric paragliding technologies
Paragliding is becoming more electric, giving people who love this exciting sport more options. The magnet is a key part of this change. Its uniq...
Show more >
Published: 2023-07-07
![]() Daniel Gårdefelt
Daniel Gårdefelt
Magnets in the advancement of smart vineyard technologies
There are always new ideas in the world of farming. From the ancient Romans improving the art of wine storage to the current use of drones for ae...
Show more >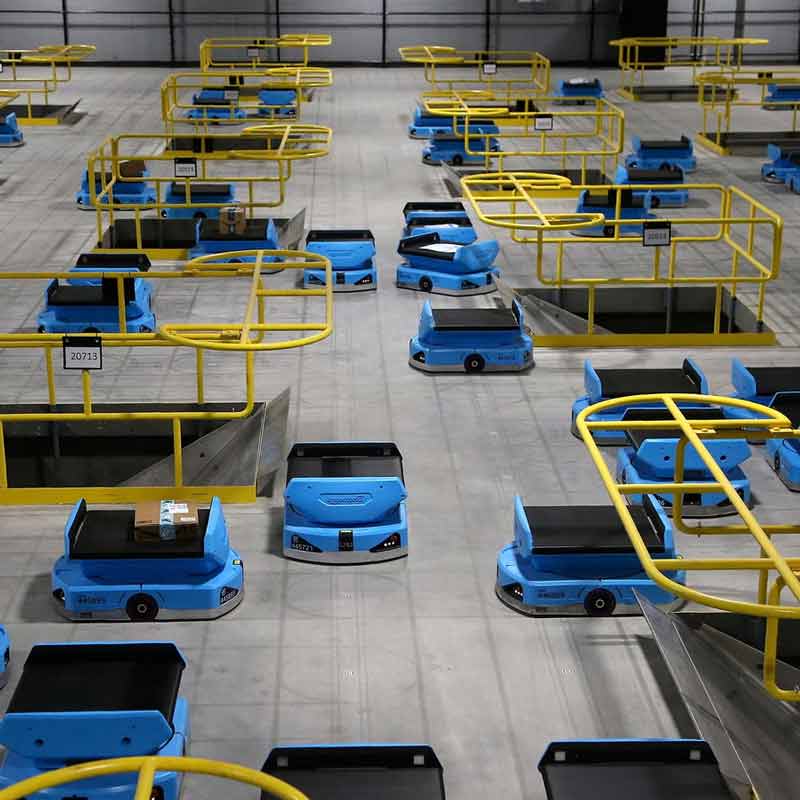
Published: 2023-07-05
![]() Daniel Gårdefelt
Daniel Gårdefelt
Magnets in advanced automated warehousing systems
As global trade grows, so does the need for warehouse systems that are both efficient and automated. Magnets are one of the tools that are being ...
Show more >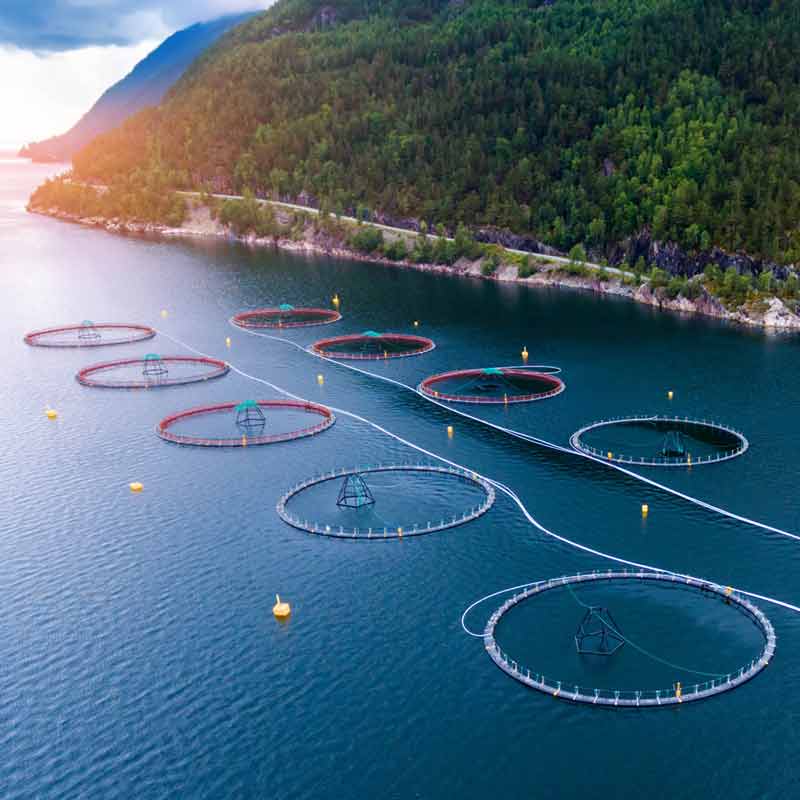
Published: 2023-07-04
![]() Daniel Gårdefelt
Daniel Gårdefelt
How magnets are influencing sustainable aquaculture technologies
Aquaculture is starting to look like a good way to feed the world in a healthy way. The practice must, however, solve big problems, and the magne...
Show more >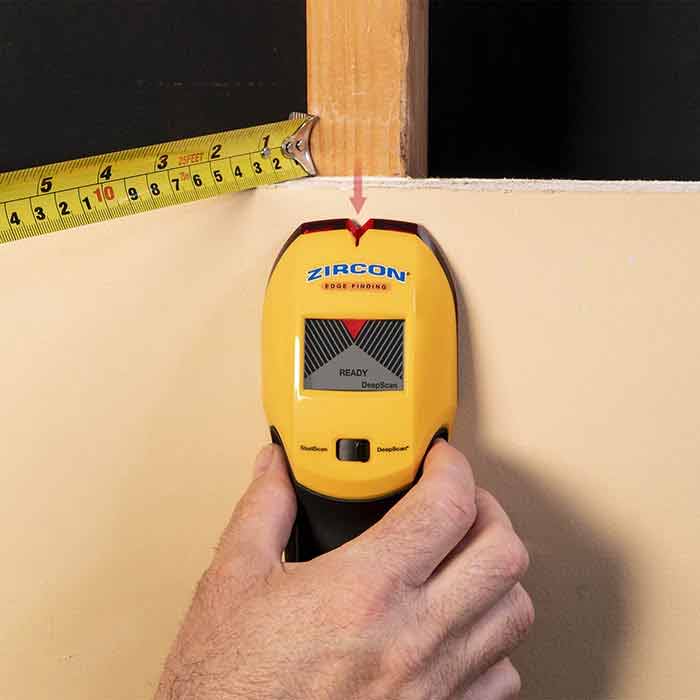
Published: 2023-07-02
![]() Daniel Gårdefelt
Daniel Gårdefelt
Hand tools with magnetic influence
Magnets are an important part of hand tools because they make them easier to use and make them work better. They have changed the way many tools ...
Show more >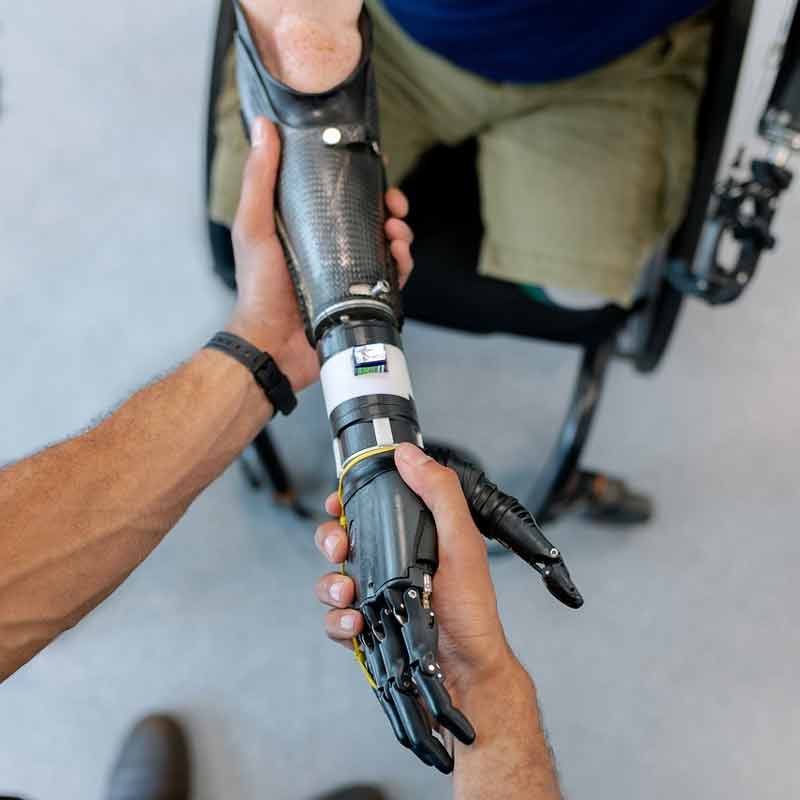
Published: 2023-06-30
![]() Daniel Gårdefelt
Daniel Gårdefelt
Magnets and the future of prosthetic limbs
Magnets play an important role in the development of prosthetic technology. Today we take a quick look at how magnets are used to improve prosthe...
Show more >
Published: 2023-06-29
![]() Daniel Gårdefelt
Daniel Gårdefelt
The role of magnets in hearing aid functionality
In the field of hearing aid, magnets play a vital role in improving their usability and user experience. Fundamentals of sound amplification: ...
Show more >
Published: 2023-06-26
![]() Daniel Gårdefelt
Daniel Gårdefelt
Magnets powering smart home innovations
The future of living - the smart home era, where ease of use, efficiency, and safety work together to make life easier and safer. Magnets is the ...
Show more >
