Recent Post

Magnets in Restaurant Kitchens

Global supply challenges and HYAB’s role

Electromagnets – a more controllable magnet

Magnetic filtration in the process industry
Sheet metal handling – Easier with magnets
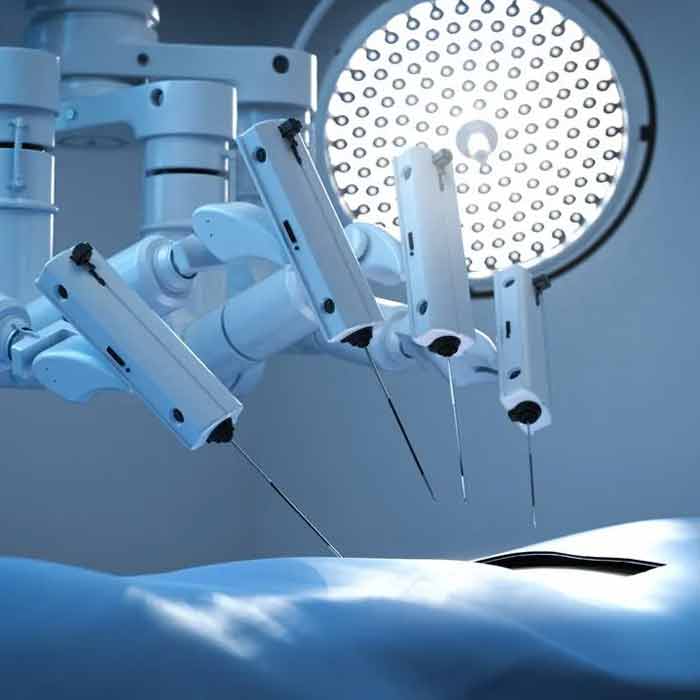
Revolutionizing robotic surgery with magnets
Published: 2023-06-16 14:05:23 • Daniel Gårdefelt
Robotic surgery, a combination of medicine and technology, has revolutionized the medical field by providing unmatched precision, control, and little intrusion. The use of magnets is one of the unsung heroes that has made this revolution possible.
Magnetic Positioning and Manipulation:
Surgery tool manipulation and positioning are made easier by magnets. Robotic systems can operate equipment with magnetic tips within the patient's body by using external magnets. As a result, there is no longer a need for several incisions, which lowers the danger of infection and speeds up recovery.
Haptic magnetic feedback:
For surgeons to feel the interaction between surgical equipment and tissues, haptic feedback is crucial. Magnets are used to make haptic feedback devices for robotic surgery. In robotic surgery, physicians can simulate the resistance and textures of tissue using magnetorheological materials, which change their properties when exposed to magnetic fields.
Medical Robotic Magnetic Levitation:
Robotic surgery is utilizing magnetic levitation (Maglev) technology to allow surgical instruments to move smoothly and without resistance. With the help of magnets, the instruments can 'float,' resulting in smoother and more accurate movements. This is especially useful for delicate procedures like eye surgery, where the highest degree of precision is required.
Transfer power wirelessly:
Through magnetic induction, magnets enable wireless power transfer, which is essential for maintaining robotic surgical equipment' electrical supply without the limitations of wires. As a result, the operating area becomes less cluttered and has fewer possible sites of contamination, creating a more sterile atmosphere.
Navigation and imaging:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), which is frequently used in conjunction with robotic surgery for real-time navigation and monitoring, depends heavily on magnets. Surgeons can execute surgeries with real-time visual guidance by merging MRI with robotic equipment, increasing outcomes and lowering risks.
Conclusion:
Surgical breakthroughs that are more precise, less intrusive, and safer are unquestionably being made possible by the incorporation of magnets into robotic surgery systems. Magnets are at the forefront of the developments transforming robotic surgery, from manipulation and haptic feedback to magnetic levitation and guided drug delivery.