Recent Post

Magnets in Restaurant Kitchens

Global supply challenges and HYAB’s role
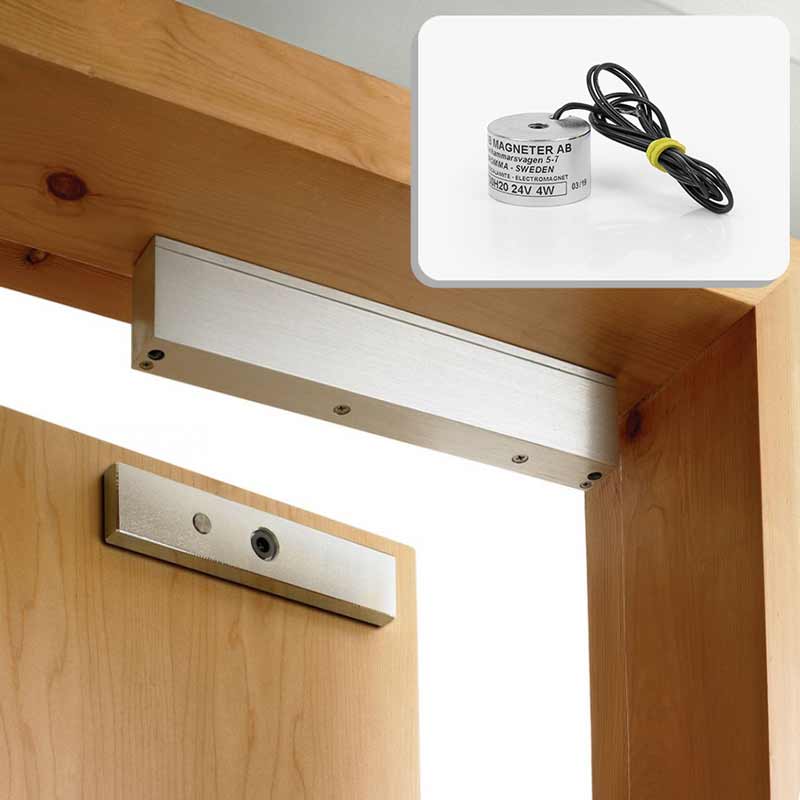

Electromagnets – a more controllable magnet
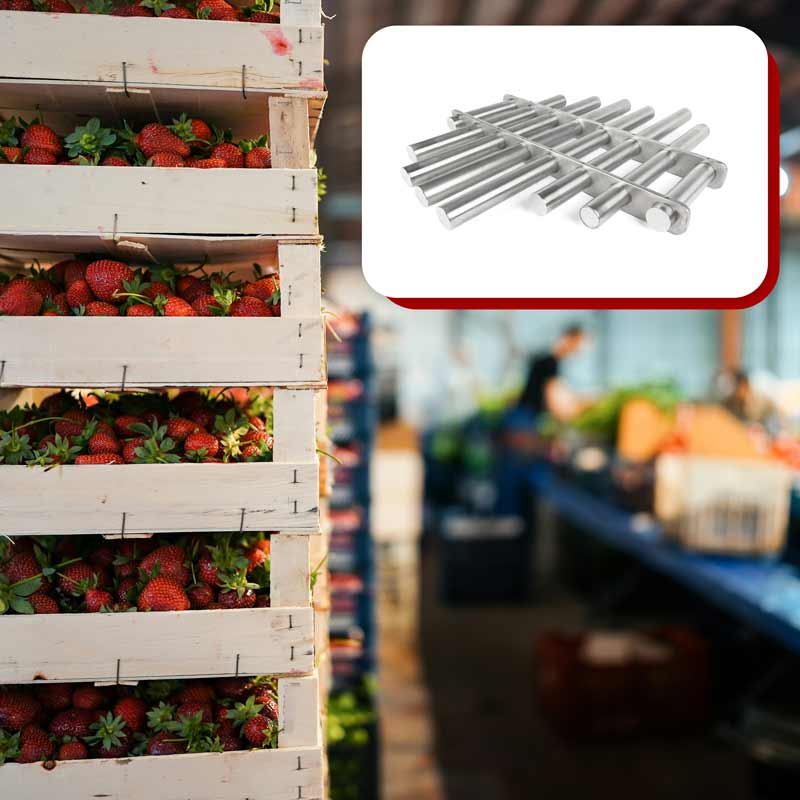

Magnetic filtration in the process industry
Sheet metal handling – Easier with magnets
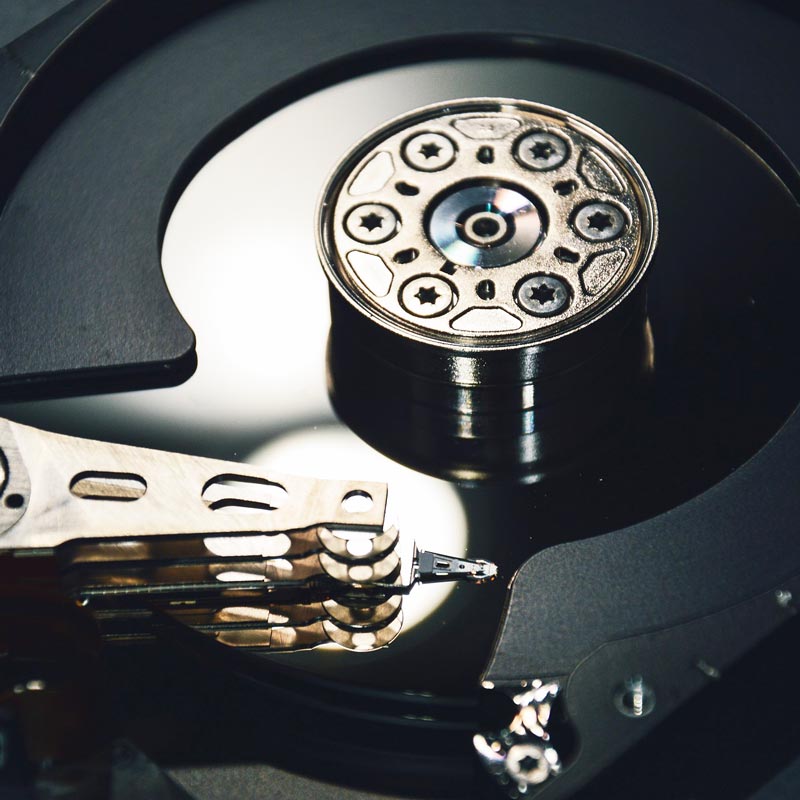
Magnets in data storage
Published: 2023-03-07 09:26:16 • Daniel Gårdefelt
Magnetic materials have long played an important role in data storage technology. Magnets have made it possible to store large amounts of information in a compact, reliable and inexpensive way, from floppy disks and hard drives to magnetic tape and memory cards. today we will go into the basics of magnetic data storage as well as the role of magnetic materials in this technology.
What is Magnetic Data Storage?
Magnetic data storage is a technology that stores and retrieves digital information using magnetic fields. This works on the basic principle that the material can be magnetized in different directions to represent binary digits (bits) of information that can be read and written using magnetic sensors. Magnetic properties of data storage materials can be optimized for high storage density, fast read and write speeds, and long-term stability.
What materials are used for data storage
The most common material used in data storage devices is ferrite, with strong, spontaneous magnetization. Iron, cobalt and nickel are examples of ferromagnetic materials, while iron oxide and other complex mixtures are examples of ferrimagnetic materials. Rare earth magnets such as neodymium and samarium-cobalt have also been used in high-performance data storage devices in recent years.
Which direction of magnetization the material is magnetized to is decisive for data storage. It is called magnetic anisotropy and can be controlled through the crystal structure and composition of engineering magnetic materials, allowing precise control of magnetic field strength and orientation. This is critical to achieve high-density magnetic storage while reducing the risk of data corruption caused by unwanted magnetic interference.
Magnetic recording media
Magnetic recording is magnetized materials used to store digital data in magnetic data storage devices. Magnetic discs, magnetic tapes, and magnetic memory cards are the most common types of magnetic recording media.
Magnetic disks, also known as hard disks, are the most common storage media used in personal computers and servers. In recent years, so-called SSD and M.2 SSD storage has caught up with regular hard drives, at least when it comes to personal computers. The classic hard drives are made up of several spinning disks that are coated with magnetic material and have read/write heads that move over the surface of the disks to read and write data. Hard drives are ideal for high-performance computers and data centers due to their high storage density, but mainly for the very low price per GB/TB compared to SSDs.
Magnetic tape is a type of traditional magnetic data storage that is still widely used for backup and archival purposes. Magnetic tape consists of a long, narrow strip of magnetic material wound around a reel and read/write heads that move across the tape to read and write data. Magnetic tapes have lower storage density and slower read/write speeds than hard drives, but they are cheaper and can store large amounts of data for longer periods of time.
Magnetic memory cards, also known as flash memory cards, are a portable and long-lasting form of magnetic data storage commonly used in digital cameras, cell phones, and other portable devices. Magnetic memory cards consist of a small, flat piece of magnetic material that contains a memory chip and read/write contacts for inserting the card into a compatible device. Magnetic memory cards have a high storage density and are ideal for portable digital data storage and transfer.
Conclusion
Magnetic materials have played an important role in the development of data storage technology, from floppy disks and magnetic tapes to hard drives and memory cards. Magnetic properties of data storage materials can be optimized to achieve high storage density, fast read and write speeds and long-term stability, making them a good choice for a wide range of computing, communication and entertainment applications.


